 |
||
| T-NS Home | Editorial Board | T-NS in IEEE Xplore | Early Access | Manuscript Submission | ||
| May 2019 FEATURE ARTICLES - THESE ARE OPEN ACCESS FOR A LIMITED TIME | ||
An Upgraded Luminosity Leveling Procedure for the ALICE Experimentby Giacinto de Cataldo, Gianluca Valentino, Antonio Franco, Reyes Alemany, Fabio Follin, Michi Hostettler, Jorg Wenninger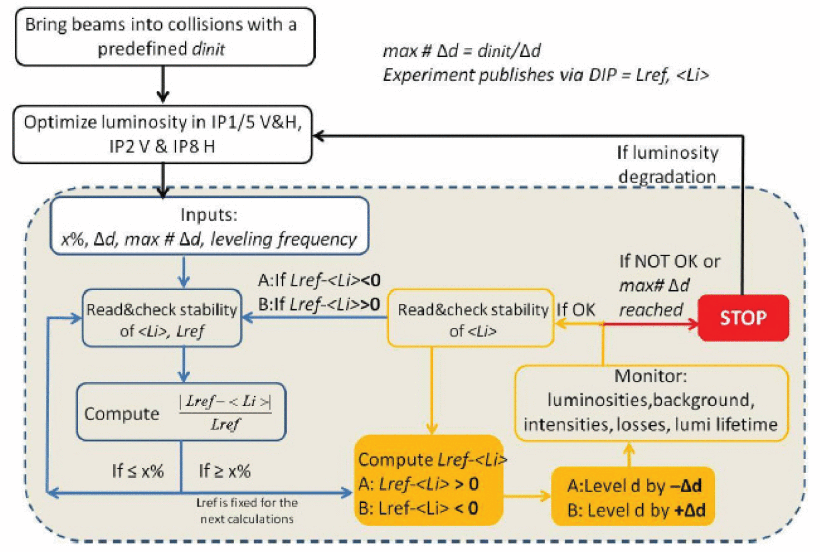 The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) Interface project (LHC_IF) ensures that the A Large Ion Collider Experiment (ALICE) can operate congruently and safely with the LHC in different machine configurations and beam modes. Measurements in proton-proton (pp) collisions are vital for ALICE and serve as a reference to calibrate the Pb ion-Pb ion (Pb-Pb) measurements. However, during the pp operation to limit the event pile up (number of pp collisions per bunch crossing) and ensure a high-quality data sample, the instantaneous luminosity must be limited in ALICE to 5 × 10 30 cm -2 s -1 . This is achieved by applying a beam-beam separation in the separation plane up to several beam σ (beam size unit), which is known as luminosity leveling. Given that the luminosity in a collider is expressed by a well-known formula in terms of parameters such as the beam separation, bunch intensities, number of colliding bunches, and beam size, then it is possible to determine the beam separation if the other parameters are known for both the target luminosity and the measured instantaneous luminosity. From the difference of the two beam separations, different step sizes spanning from 0.5 σ down to 0.025 σ are calculated and transmitted to LHC that accordingly steers the beams until the instantaneous luminosity smoothly reaches the target within ± 5%. In this note, the results achieved with the new beam-leveling procedure over almost a year of operation, as well as comparisons with simulations, are presented. more... |
||
Damage Separation in a Bipolar Junction Transistor Following Irradiation With 250-MeV Protonsby Steven C. Witczak, Scott R. Messenger, Daniel M. Fleetwood, Ronald D. Schrimpf, Michael S. Langlois, M. Codie Mishler, Dennis A. Adams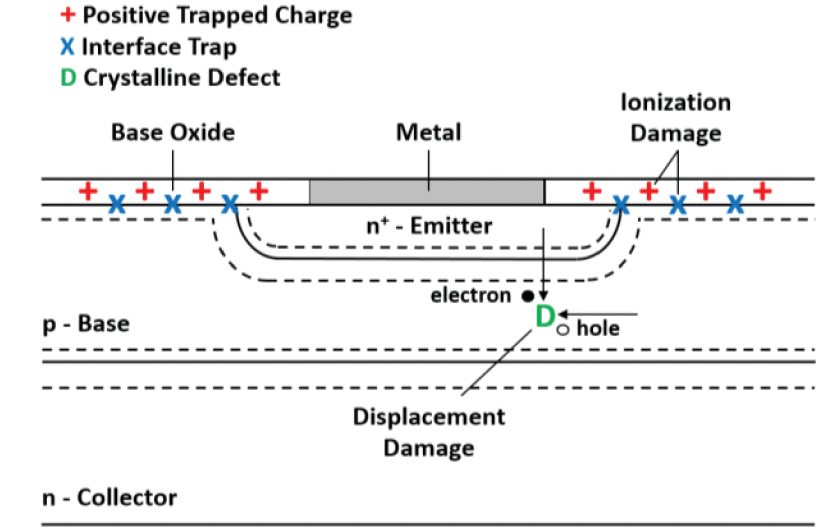 Irradiation of 2N5339 n-p-n bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) with either 250-MeV protons or 10-keV X-rays shifts the input characteristics to lower values of V BE while degrading the current gain and drive current. The degradation is consistent with increased recombination in the neutral base and emitter-base (E-B) depletion region. A decrease in collector current following proton irradiation suggests that recombination in the neutral base is significant. At a given ionizing dose, degradation is worse for proton irradiation than for X-ray irradiation due to the presence of displacement damage and a higher charge yield. A comparison of degradation produced by the two radiation sources suggests that ~40% of the excess base current resulting from 250-MeV proton irradiation is due to ionization damage. When compared with previous results for other devices, these results suggest that ionization-to-displacement damage ratios in bipolar devices may increase with proton energy in a way that is consistent with trends in charge yield and non-ionizing energy loss (NIEL).more... |
||
 |
||
A PUBLICATION OF THE IEEE NUCLEAR AND PLASMA SCIENCES SOCIETY |
||
| May 2019 | VOLUME 66 | NUMBER 4 | IETNAE | (SSN 0018-9499) | ||
REGULAR PAPERS
Home |
Contact & Support |
Accessibility |
Nondiscrimination Policy |
Feedback |
Privacy and Opting Out of Cookies
© Copyright 2019 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this website signifies your agreement to the IEEE Terms and Conditions. A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. If you have questions about this mailing, or need assistance, please direct your inquiries to the IEEE Contact Center. Replies to this message do not reach IEEE. |
||